2018 Income levels for Dual Eligible Medicare Medi-Cal beneficiaries in California.
The 2018 guidelines reflect the 2.1 percent price increase between calendar years 2016 and 2017. After this inflation adjustment, the guidelines are rounded and adjusted to standardize the differences between family and household sizes. Included with this informational bulletin is the 2018 Dual Eligible Standards chart that displays the new standards for the Medicare Savings Program categories. These standards are also available on Medicaid.gov at https://www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/eligibility/medicaid-enrollees/index.html.
Income Levels Increase For Dual Eligible Medicare Medi-Cal Beneficiaries
The asset limits are not derived from the poverty levels but are instead related to the Medicare Low-Income Subsidy asset limits. Please note that the income figures for the Qualified Disabled Working Individual (QDWI) program identified in the chart incorporate earned income disregards, in addition to the $20 general income disregard.
2018 Dual Eligible Standards
(Based on Percentage of Federal Poverty Levels)
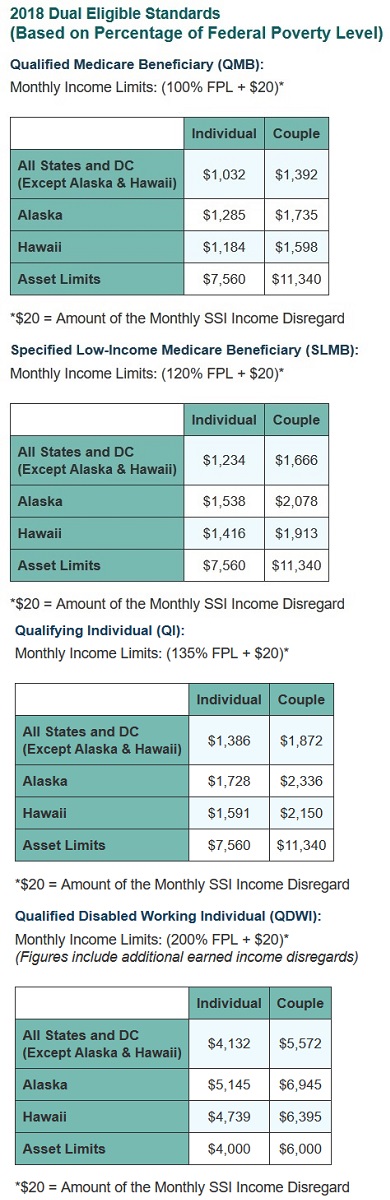
2018 income levels for Qualified Medicare Beneficiary, Specified Low-Income, Qualifying Individual, and Qualified Disabled Working Individual.
Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB):
Monthly Income Limits: (100% FPL + $20)*
- All States and DC (Except Alaska & Hawaii): $1,032 – Individual $1,392 – Couple
- Alaska: $1,285 – Individual $1,735 – Couple
- Hawaii: $1,184 – Individual $1,598 – Couple
- Asset Limits: $7,560 – Individual $11,340 – Couple
Specified Low-Income Medicare Beneficiary (SLMB):
Monthly Income Limits: (120% FPL + $20)*
- All States and DC (Except Alaska & Hawaii): $1,234 – Individual $1,666 – Couple
- Alaska: $1,538 – Individual $2,078 – Couple
- Hawaii: $1,416 – Individual $1,913 – Couple
- Asset Limits: $7,560 – Individual $11,340 – Couple
Qualifying Individual (QI):
Monthly Income Limits: (135% FPL + $20)*
- All States and DC (Except Alaska & Hawaii): $1,386 – Individual $1,872 Couple
- Alaska: $1,728 – Individual $2,336 – Couple
- Hawaii $1,591 – Individual $2,150 – Couple
- Asset Limits: $7,560 – Individual $11,340 – Couple
Qualified Disabled Working Individual (QDWI):
Monthly Income Limits: (200% FPL + $20)*
(Figures include additional earned income disregards)
- All States and DC (Except Alaska & Hawaii): $4,132 – Individual $5,572 – Couple
- Alaska: $5,145 – Individual $6,945 – Couple
- Hawaii: $4,739 – Individual $6,395 – Couple
- Asset Limits: $4,000 – Individual $6,000 – Couple
*$20 = Amount of the Monthly SSI Income Disregard
Seniors & Medicare and Medicaid Enrollees
Medicaid provides health coverage to more than 4.6 million low-income seniors, nearly all of whom are also enrolled in Medicare. Medicaid also provides coverage to 3.7 million people with disabilities who are enrolled in Medicare. In total, 8.3 million people are “dually eligible” and enrolled in both Medicaid and Medicare, composing more than 17% of all Medicaid enrollees. Individuals who are enrolled in both Medicaid and Medicare, by federal statute, can be covered for both optional and mandatory categories.
What Medicaid Covers for Medicare Enrollees
Medicare has four basic forms of coverage:
- Part A: Pays for hospitalization costs
- Part B: Pays for physician services, lab and x-ray services, durable medical equipment, and outpatient and other services
- Part C: Medicare Advantage Plan (like an HMO or PPO) offered by private companies approved by Medicare
- Part D: Assists with the cost of prescription drugs
Medicare enrollees who have limited income and resources may get help paying for their premiums and out-of-pocket medical expenses from Medicaid (e.g. MSPs, QMBs, SLBs, and QIs). Medicaid also covers additional services beyond those provided under Medicare, including nursing facility care beyond the 100-day limit or skilled nursing facility care that Medicare covers, prescription drugs, eyeglasses, and hearing aids. Services covered by both programs are first paid by Medicare with Medicaid filling in the difference up to the state’s payment limit.
2018 Federal Poverty Levels Medicaid Dual Eligible
Included with this informational bulletin is the 2018 Dual Eligible Standards chart that displays the new standards for the Medicare Savings Program categories.