Few people outside of the North Fork Ditch Company knew or understood how much work Loring K. Jordan put into the water system. He took over a fragile water canal, and in the face of increasing water demand, was able to keep the water flowing.
Kevin Knauss: Health, History, Travel, Insurance
Posts related to the North Fork Ditch on the North Fork of the American River.



Dear Sir, I did not get yours of yesterday until 11/2 o’clock P.M. Consequently, you will not hear from me until tomorrow morning unless I should get a chance to send this to you this evening. The reason that I did not get it is this – The canal broke about one mile below this place about 8 o’clock last night. Consequently, I was not here when the stage came in and Mr. Baldwin gave you letter to Woods and he did not give it to me until this afternoon.



From my car at the Oregon Bar parking lot, to the point where I estimated the first tunnel was located, is a little over 2.65 miles. However, those 2 miles, along the river, over the river cobble, cliffs, and sand bars is some of the most challenging and strenuous terrain I have hiked over. There are points where bare rock juts into the river and you must literally climb up and over the slate or granite.


Isaac Hinkle was 25 years old and working on his father’s farm in Indiana in 1880. His older brother Amos had left the farm for California and Isaac decided to follow him in 1881. By 1882 Isaac was a registered voter in Sacramento County’s Mississippi Township. In 1885 Isaac married Jessie Brown and would have a long marriage with Jessie for the next 48 years. Also in 1885 Isaac Hinkle would make his first land purchase. He bought land in the town of Ashland from John Cardwell who was a large owner of in the area for $850. Even though the land was within the Public Land Survey System of Townships and Ranges, the deed refers to original metes and bounds description before the 1865 official survey map.


By the time of the Army Corp report conducted its inventory most of the North Fork Ditch had been lined with concrete. Many of the appurtenances were also concrete such as wasteways, intake structures and sluice gates. Of the 37 flumes, 32 were constructed of timber and only 5 were metal. The timber flume construction allowed them to be built with small changes or bends in the direction to navigate around boulders and hillsides. The metal flumes, by contrast, were best adapted to spanning a small ravine in a straight line.


With Folsom Lake water levels low in the autumn of 2016, I decided to hike from Rattlesnake Bar up the North Fork of the American River to see if I could catch glimpses of gold rush era history. The terrain was far more difficult than I imagine. While I know the river canyon has change since the gold rush of 1849, I was surprised at just how arduous the hiking along this stretch of the river must have been for the gold miners.

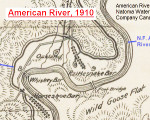
For history buffs there is nothing closer to heaven than examining an old map. I share that fascination and also enjoy sharing old maps that I’ve found. Recently I uploaded a map published in 1910 by the American River & Natomas Water & Mining Company illustrating their network of canals. The map is generally topographically accurate and includes some place names not found on previous or later topographical maps.

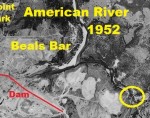
Even before Folsom Lake Dam was built and the reservoir filled, the north fork of the American River was supplying water to communities, farms and ranches in south Placer and northeast Sacramento counties. I recently found aerial photography from 1952 showing a free flowing north and south fork of the American River. Finally, I can […]


Spam prevention powered by Akismet